|
Static Translation
To configure static inside source address translation, perform the
tasks in Figures
 and and
 . .
Figure
 shows the
use of static NAT translation. The router will translate packets from
host 10.1.1.2 to a source address of 192.168.1.2. shows the
use of static NAT translation. The router will translate packets from
host 10.1.1.2 to a source address of 192.168.1.2.
Dynamic Translation
To configure dynamic inside source address translation, perform the
tasks in Figure
 . .
The access list must
permit only those addresses that are to be translated. Remember that
there is an implicit “deny all” at the end of each access list. An
access list that is too permissive can lead to unpredictable results.
Cisco advises against configuring access lists referenced by NAT
commands with the
permit any
command. Using
permit any
can result in NAT consuming too many router resources, which can cause
network problems.
Figure
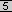 translates
all source addresses passing access list 1, which have source address
from 10.1.0.0/24, to an address from the pool named nat-pool1. The
pool contains addresses from 179.9.8.80/24 to 179.9.8.95/24. translates
all source addresses passing access list 1, which have source address
from 10.1.0.0/24, to an address from the pool named nat-pool1. The
pool contains addresses from 179.9.8.80/24 to 179.9.8.95/24.
Note: NAT will not
translate the host 10.1.1.2, as it is not permitted for translation
by the access list.
Overloading
Overloading is configured in two ways depending on how public IP
addresses have been allocated. An ISP can allocate a network only one
public IP address, and this is typically assigned to the outside
interface which connects to the ISP. Figure
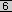 shows how
to configure overloading in this situation. shows how
to configure overloading in this situation.
Another way of configuring overload is if
the ISP has given one or more public IP addresses for use as a NAT
pool. This pool can be overloaded as shown in the configuration in
Figure
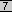 . .
Figure
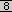 shows an example configuration of PAT.
shows an example configuration of PAT.
| |
 Lab Activity
Lab Activity
Lab Exercise: Configuring NAT
In this lab, a router will be
configured to use network address translation (NAT).
|
|
|
| |
 Lab Activity
Lab ActivityLab Exercise: Configuring PAT
In this lab, a router will be configured to use Port Address
Translation (PAT).
|
|
|
| |
 Lab Activity
Lab ActivityLab Exercise: Configuring static NAT Addresses
In this lab, a router will be
configured to use network address translation (NAT) to convert
internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside
public addresses.
|
|
|
| |
 Lab Activity
Lab Activity
e-Lab Activity: Configuring NAT
In this lab, the student will configure
NAT.
|
|
| |
 Lab Activity
Lab Activity
e-Lab Activity: Configuring PAT
In this lab, the students will configure a router to use Port
Address Translation (PAT) to convert internal IP addresses,
typically private addresses, into an outside public address
|
|
| |
 Lab Activity
Lab Activity
e-Lab Activity: Configuring Static NAT Addresses
In this lab, the student will configure
a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert
internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside
public addresses.
|
|
|